Wondering why your laptop gets so hot or how to stop it from overheating? Keeping your laptop cool is important for both comfort and performance. When your device overheats, it can slow down, shut off unexpectedly, or even cause long-term damage. Here’s how to fix an overheating laptop and keep it running smoothly.
See also -12 Computer Updates You Should Never Skip (And Why)
What to Know
- Clean air vents and fans regularly to remove dust buildup that blocks airflow
- Use your laptop on hard, flat surfaces and consider a cooling pad for better ventilation
- Adjust power settings to reduce CPU usage and lower heat generation
- Monitor temperatures with built-in tools and close unnecessary background programs
- Keep your environment cool and avoid direct sunlight or hot surfaces
Understanding Laptop Overheating
Laptop overheating occurs when your device’s cooling system can’t manage heat effectively : one of the most common reasons why a laptop gets so hot so fast. Modern laptops pack powerful processors into compact spaces, making thermal management challenging.
Common signs of overheating include:
- Fan running constantly at high speeds
- Laptop becoming uncomfortably hot to touch
- Unexpected shutdowns or performance slowdowns
- Loud fan noise during normal tasks
- Screen brightness automatically dimming
Why this matters: Overheating can cause permanent damage to internal components, reduce battery lifespan, trigger thermal throttling that slows performance, and in extreme cases, cause complete system failure.
Clean Your Laptop's Cooling System
1. Shut down and unplug your laptop
Power off your laptop completely and disconnect the charging cable. Allow the device to cool down for at least 30 minutes before cleaning.
2. Clean external air vents
Locate the air vents on your laptop's sides and back. Use compressed air to blow out dust and debris from the vents. Hold the can upright and use short bursts rather than continuous spraying.
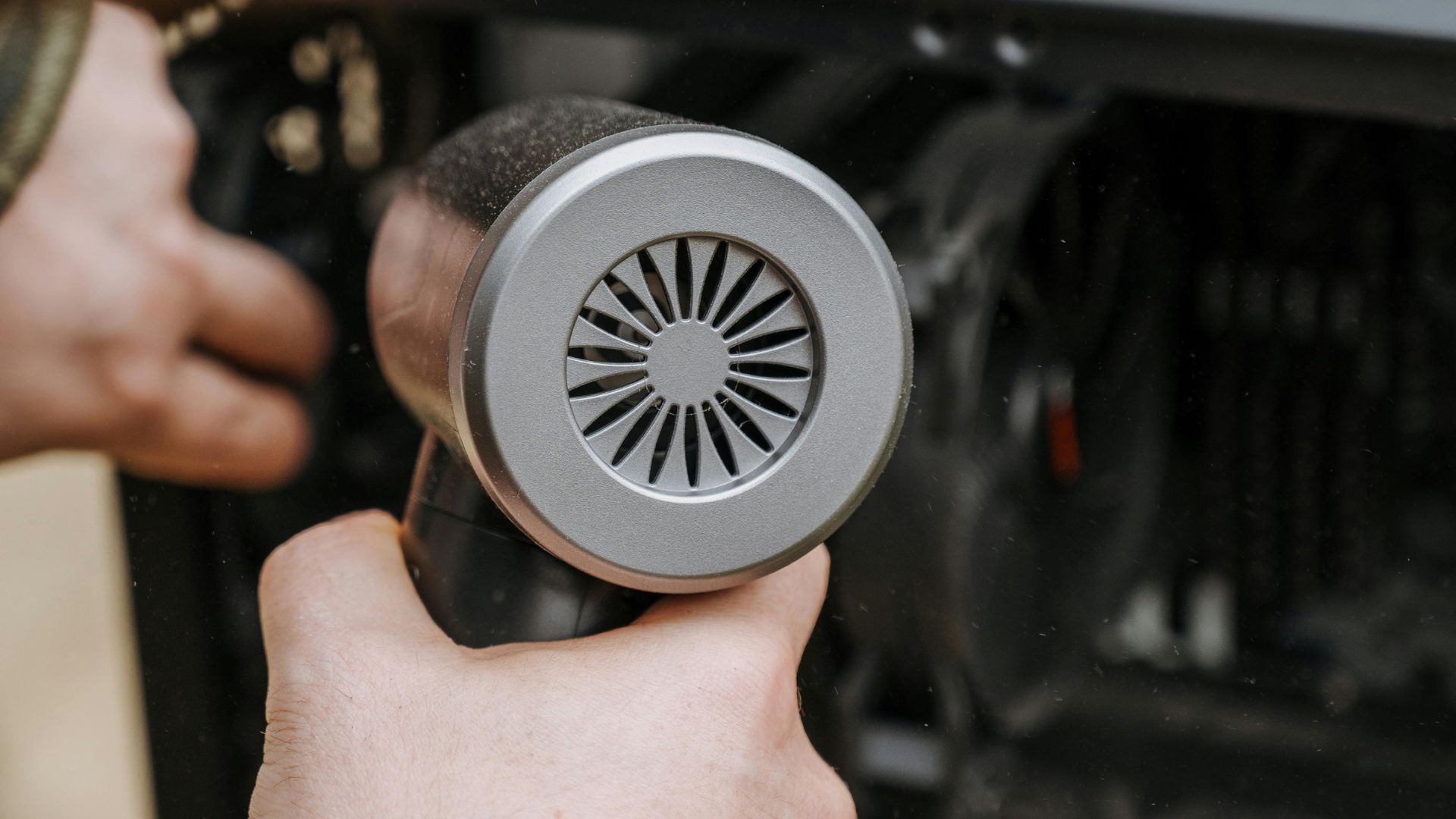

3. Clean the fan area
Direct compressed air into the fan vents to dislodge dust stuck inside the fan blades. This prevents the fan from working harder than necessary to move air through the system.
Why this matters: According to Dell's overheating prevention guide, dust accumulation is one of the primary causes of laptop overheating. A single layer of dust can reduce cooling efficiency by up to 40%, forcing your laptop to work harder and generate more heat.
See also - Should You Leave Your Laptop Plugged In All the Time?
Optimize Your Laptop's Environment
If you’re trying to figure out how to cool down your laptop, start with your setup and environment.
4. Use your laptop on hard surfaces
Place your laptop on hard, flat surfaces like desks or tables instead of soft surfaces like beds, couches, or your lap. Soft surfaces can block air vents and trap heat.
5. Invest in a cooling pad
Purchase a laptop cooling pad with built-in fans to improve air circulation around your device. These stands elevate your laptop and provide additional airflow to the bottom vents.
6. Control your environment
Keep your workspace cool and well-ventilated. Avoid using your laptop in direct sunlight or hot environments. Position it away from heat sources like radiators or direct sunlight through windows.
Why this matters: Proper ventilation allows your laptop's cooling system to work efficiently. Even a few degrees of ambient temperature reduction can significantly impact your laptop's internal temperatures.
See also -10 Files on Your Computer That Can Damage Your Hard Drive
Adjust System Settings
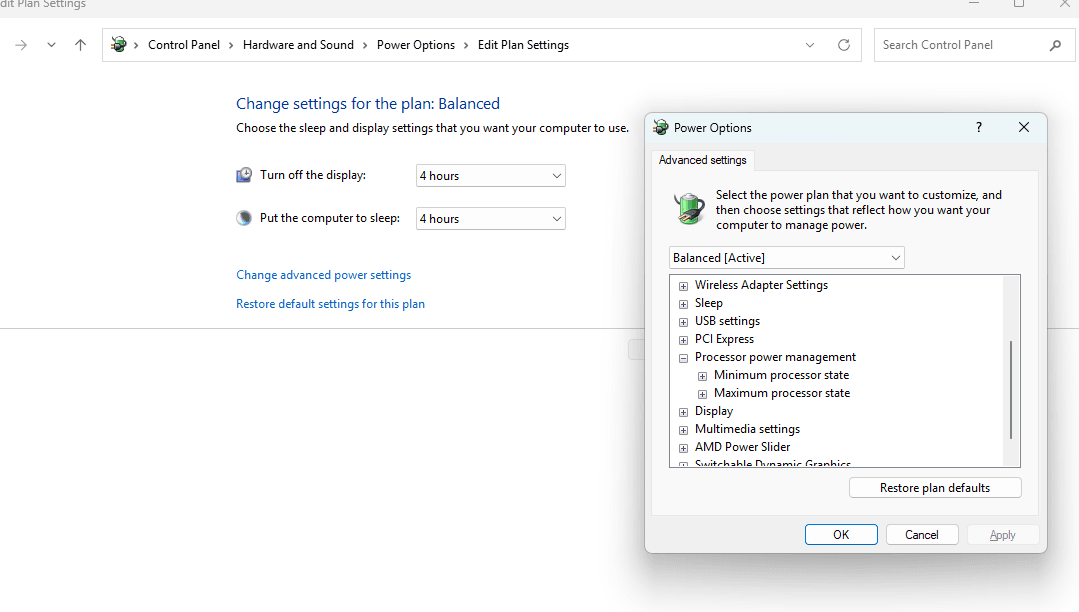
7. Modify power settings
Open Control Panel and navigate to Power Options. Click "Change plan settings" for your current power plan, then select "Change advanced power settings."
8. Reduce maximum processor state
Find "Processor power management" in the advanced settings and expand it. Locate "Maximum processor state" and reduce both "On battery" and "Plugged in" settings from 100% to 85% or lower.
According to one user's experience with Dell laptop overheating, changing both settings to 85% can significantly reduce thermal issues without noticeably impacting performance for most tasks.
9. Enable power saving mode
Switch to a power-saving mode when performing less demanding tasks. This reduces CPU usage and heat generation without significantly impacting performance for basic activities.
Why this matters: Limiting maximum processor performance prevents your CPU from running at full capacity constantly, which can reduce temperatures by 20+ degrees Celsius while maintaining adequate performance for most tasks.
Monitor and Manage System Performance
10. Check running programs
Open Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc) and review the Processes tab. Close unnecessary programs that consume high CPU or memory resources, especially browser tabs with video content or resource-intensive applications.
11. Update drivers and software
Keep your operating system, drivers, and software updated. Manufacturers often release updates that improve thermal management and fix performance issues.
12. Monitor temperatures
Use built-in monitoring tools or download free temperature monitoring software like HWMonitor, Core Temp, or Speccy to track your laptop's internal temperatures and identify problematic patterns. According to Tom's Hardware's CPU temperature guide, most laptops can safely operate at CPU temperatures up to 80-90°C, but sustained temperatures above 85°C indicate potential overheating.
Why this matters: Background processes can consume significant system resources even when you're not actively using them. A single poorly optimized program can cause your CPU to work at high capacity continuously.
FAQ
Q: What temperature is too hot for a laptop?
A: Most laptops can safely operate at CPU temperatures up to 80-90°C, but sustained temperatures above 85°C indicate potential overheating. Ideal operating temperatures are between 40-70°C under normal use.
Q: How often should I clean my laptop's fans?
A: Clean your laptop's external vents monthly and perform more thorough internal cleaning every 3-6 months, depending on your environment's dust levels and usage patterns.
Q: Can I use my laptop while it's overheating?
A: Avoid using an overheating laptop as it can cause permanent damage to internal components. Turn off the device, let it cool down, and address the overheating cause before resuming use.
Q: Do cooling pads actually work?
A: Yes, quality cooling pads with active fans can reduce laptop temperatures by 5-15C by improving airflow around the device. They're particularly effective for laptops with bottom air intake vents.
Q: Will reducing processor speed affect gaming performance?
A: Reducing maximum processor state to 85% typically won't noticeably impact gaming performance, as most games don't require sustained 100% CPU usage. However, intensive tasks like video rendering may take slightly longer to complete.
Q: Why is my laptop overheating so fast?
A: This can happen when the cooling system is blocked by dust or when high CPU usage keeps your laptop running at full power. Cleaning the vents and adjusting power settings can help your laptop cool down faster.
Troubleshooting Persistent Overheating
If you’ve tried everything and your laptop is still overheating, here’s how to fix an overheating laptop for good.
If your laptop continues overheating after following these steps:
- Check for malware: Run a full system antivirus scan to identify resource-consuming malicious software
- Consider professional cleaning: Internal dust removal may require disassembling your laptop, which should be done by experienced technicians
- Evaluate hardware issues: Failing fans, dried thermal paste, or damaged heat sinks may need professional repair or replacement
- Monitor specific components: Use diagnostic tools to identify whether the CPU, GPU, or other specific components are causing excessive heat generation
Professional repair may be necessary if the thermal paste between your CPU and heat sink has dried out, typically after 2-3 years of use, or if internal fans have failed completely.